The Witness Tree Project | The Witness Trees | Castanea sativa
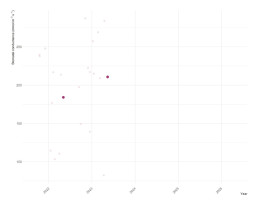
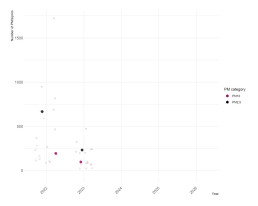
Castanea sativa, or sweet chestnut, is native to the Balkan Peninsula to Iran. As it is adapted to hotter climates [1], is it interesting to observe in the context of a changing climate. Sweet chestnut is a culturally important species and has been cultivated as a source of food for its edible starchy nuts for over two thousands years, and also for its wood [2]. It is also a species that is widely researched globally, with more than 200 of its features being studied, as retrieved from relevant databases.
The tree at the garden has an individual value, as a fine specimen tree from the collection.
1. Conedera, M., Tinner, W., Krebs, P., de Rigo, D., Caudullo, G., 2016. Castanea sativa in Europe: distribution, habitat, usage and threats. In: San-Miguel-Ayanz, J., de Rigo, D., Caudullo, G., Houston Durrant, T., Mauri, A. (Eds.), European Atlas of Forest Tree Species. Publ. Off. EU, Luxembourg, pp. E0125e0+
2. Conedera, Marco & Tinner, W. & Krebs, Patrik & de Rigo, Daniele & Caudullo, Giovanni. (2016). Castanea sativa in Europe: distribution, habitat, usage and threats.